Reinforcement Learning introduction
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a machine learning technique that combines ideas from two fields of mathematics (dynamic programming and supervised learning) to train agents to accomplish specific tasks by being placed in a dynamic environment and being allowed to interact with it via a certain sequence of actions, given a set of observations and an established reward system. RL differs fundamentally from supervised learning in that no input-output pairs are needed. The learning agent is not told which actions to take, but instead has to discover potential solutions by maximizing rewards through trial and error. A reward is given upon successful completion of a given task. The decisions taken by the agent gradually fine-tune its policy for accomplishing the defined task, by continuously aiming to maximize reward.
In the diagram below, the dog (the agent) observes signals from the trainer and tries to update its response (policy) to the provided cues. In this case, the environment is defined by the available space and the human - who gives a positive feedback to the agent upon satisfactory responses (or negative/no reward upon failure). ref
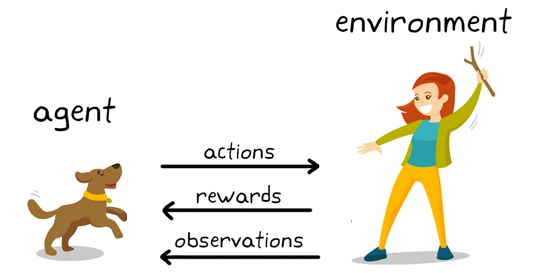
Figure 1. Overview of reinforcement learning, where the agent updates its actions based on observations and feedback from its environment. source

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.