Semi-supervised Learning Introduction
Semi-supervised learning is a class of supervised learning tasks and techniques that also make use of unlabeled data for training – typically a small amount of labeled data with a large amount of unlabeled data. Semi-supervised learning falls between unsupervised learning (without any labeled training data) and supervised learning (with completely labeled training data). It has been found that unlabeled data, when used in conjunction with a small amount of labeled data, improve the learning accuracy. In contrast with labeled data, unlabeled data are easy to produce and cheap. (Theodoridis and Koutroumbas, 2009).
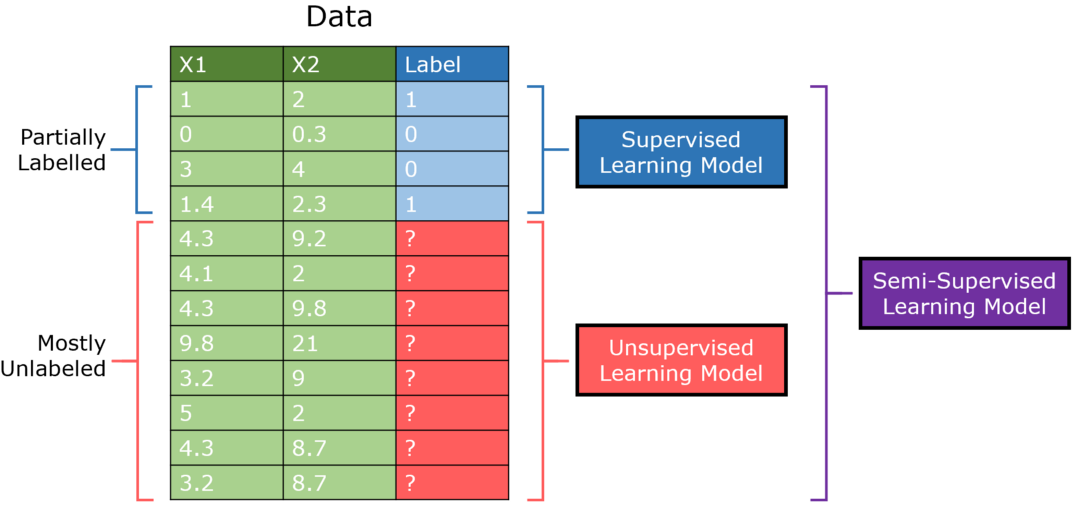
Link to image source:
There are many applications of semi-supervised algorithms in bioinformatics. This approach has been used for disease gene prediction (Thanh and Tu, 2007), gene ontology terms prediction (Jaramillo-Garzón et al, 2016) and the identification of molecular phenotypes (Roder et al, 2019) among many others.
Over the years, a large number of semi-supervised learning approaches and algorithms have been proposed. Some of these are briefly explained in the left drop-down menu section entitled “Common algorithms of semi-supervised learning”.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.